With anode positive with respect to cathode, a thyristor can be turned on by any one of the following techniques.
We know that SCR includes two stable states namely forward conduction and forward blocking.
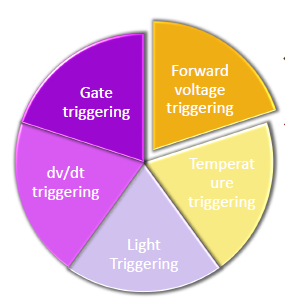
SCR triggering method can be defined as, when the SCR is switching in forward blocking state to forward conduction state which means OFF state to ON state, then it is termed as SCR turn ON methods or SCR triggering.
Forward voltage triggering
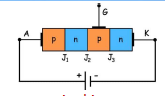
It is like forward conduction mode of SCR with gate terminal is open .
Temperature Triggering
Temperature triggering of thyristors mainly occurs when the voltage across the J2 junction as well as leakage current can increase the junction’s temperature.
When the temperature increases then it will increase the leakage current
This increasing method can be adequate to activate the thyristor, even though it tends to simply happen as the temperature of the device is high.
Light triggering
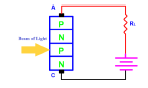
If a beam of light falls on the junction J2 of the SCR, it generates the electron-hole pairs
❖ The generated minority carriers across the blocking junction J2 and reach P2 EEE – 2020 Dr M Balasubbareddy, CBIT, Hyderabad
❖ Due to high electric field, minority carriers are accelerated and strike the covalent bond of silicon wafer and generate more electron-hole pairs
❖ So, the regenerative action takes place and the device is turned on. This method of triggering is used in light activated SCR (LASCR) and HVDC transmission systems.
dv/dt triggering
If the rate of rise of anode to cathode voltage is high, the charging current through the capacitive junction is high enough to turn on the thyristor.
A high value of charging current may destroy the thyristor hence the device must be protected against high dv/dt.
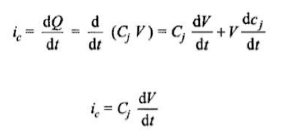
Gate triggering
❖ Turning of SCR by gate triggering is simple, reliable and efficient, it is therefore the most usual method of firing the SCRs
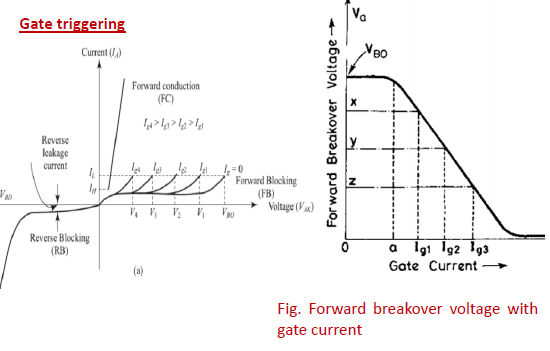
❖ A thyristor with VBO (say 800 V) higher than the normal working voltage (say 400 V) is chosen
❖ This means that thyristor will remain in forward blocking state with normal working voltage across anode and cathode with gate open.
❖ With gate current thus established, charges are injected into the inner p layer and voltage at which forward breakover occurs is reduced.
❖ The forward voltage at which the device switches to on-state depends upon the magnitude of gate current.
❖ Higher the gate current, lower is the forward breakover voltage
❖ When positive gate current is applied, gate P layer is flooded with electrons from the cathode
❖ This is because cathode N layer is heavily doped as compared to gate Player. As the thyristor is forward biased, some of these electrons reach junction J2.
❖ As a result, width of depletion layer around juntion J2 to breakdown at an applied voltage lower than forward breakover voltage VBO.
❖ If magnitude of the gate current is increased, more electrons will reach junction J2, therefore thyristor will get turned on at a much lower forward applied voltage.
Password: Turn-onmethods
pdf made by Dr M Balasubbareddy
