❖ A forward biased thyristor can be turned on by applying a positive voltage between gate and cathode terminal.
❖ But it takes some transition time to go from forward blocking mode to forward conduction mode
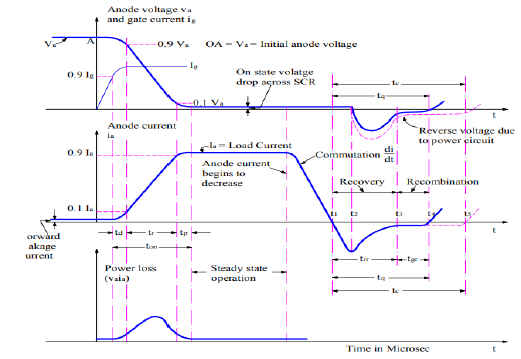
❖ This transition time is called turn on time of SCR and it can be subdivided into three small intervals as delay time (td) rise time(tr), spread time(ts).
❖ delay time (td)
❖ rise time(tr)
❖ spread time(ts)
ton = td + tr +ts
Delay Time of SCR
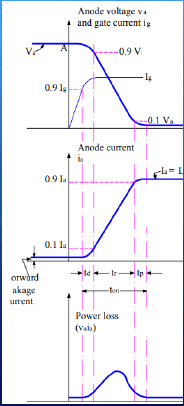
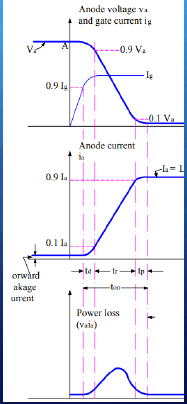
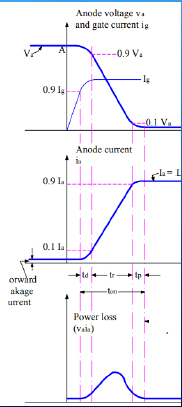
❖ Delay time of SCR can be defined as the time taken by the gate current to increase from 90% to 100% of its final value.
❖ From another point of view, delay time is the interval in which anode current rises from forward leakage current to 10% of its final value and at the same time anode voltage will fall from 100% to 90% of its initial value.
Rise Time of SCR
❖ Rise time of SCR in the time taken by the anode current to rise from 10% to 90% of its final value. At the same time anode voltage will fall from 90% to 10% of its initial value Va.
❖ The phenomenon of decreasing anode voltage and increasing anode current is entirely dependent upon the type of the load.
Spread Time of SCR
❖ It is the time taken by the anode current to rise from 90% to 100% of its final value.
❖ At the same time the anode voltage decreases from 10% of its initial value to smallest possible value.
❖ In this interval of time conduction spreads all over the area of cathode and the SCR will go to fully ON State. Spread time of SCR depends upon the cross-sectional area of cathode.
Turn OFF Time of SCR
❖ Once the thyristor is switched on or in other point of view, the anode current is above latching current, the gate losses control over it.
❖ That means gate circuit cannot turn off the device. For turning off the SCR anode current must fall below the holding current Dynamic Characteristics of SCR.
❖ After anode current fall to zero we cannot apply forward voltage across the device due to presence of carrier charges into the four layers.
❖ So turn off time of SCR can be defined as the interval between anode current falls to zero and device regains its forward blocking mode.
❖ Based on removing carrier charges from the four layers, turn off time of SCR can be divided into two-time regions,
❖ Reverse Recovery Time (trr), Gate Recovery Time (tgr)
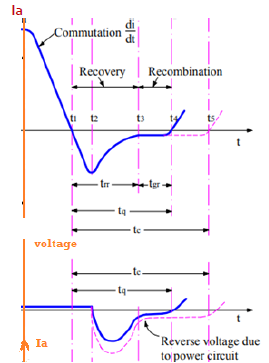
Reverse recovery time
❖ It is the interval in which charge carriers remove from J1, and J3 junction
❖ At time t1, anode current falls to zero and it will continue to increase in reverse direction with same slope (di/dt) of the forward decreasing current Dynamic Characteristics of SCR.
❖ This negative current will help to sweep out the carrier charges from junction J1 and J3
❖ At the time t2 carrier charge density is not enough to maintain the reverse current hence after t2 this negative current will start to decrease.
❖ The value of current at t2 is called reverse recovery current
❖ Due to rapid decreasing of anode current, a reverse spike of voltage may appear across the SCR.
Password: Lec-6 Dynamic
pdf made by Dr M Balasubbareddy
